1. Crushing ores.
2. Classification.
1. Crushing ores.
The ore enters the processing plant in pieces of varying sizes ranging from 200 to 300 mm to 1,500 mm, depending on the type of ore and its extraction. These pieces are made of mineral splices and can not be enriched.
 |
| Large chunk are reduced in size |
The crushing can be done in several ways: crushing, attrition, cracking, hitting, and a combination of the above methods. In some cases, they are associated with another side effect of breaking or bending forces.
Crushing is one of the most expensive processes. In process plants, the cost of the crushing process is on average 40% of the cost of minerals, while the cost of shredding equipment is about 60% of the equipment cost. The principle of fragmentation is therefore "do not overwrite". Following this principle results in energy savings, increased plant productivity, less waste of useful minerals, and less wear on breaker parts.
To respect the "override nothing" principle, the entire crushing process is divided into several stages or processes. Before each milling step, a classification is made to isolate the small items so as not to retransmit the pieces of size to be shredded. If possible, enrichment is performed after each grinding step.
Distinction: large size reduction: during crushing of ore from 1500 to 100-400 mm; Average grinding: from 400-100 to 30-50 mm and fine grinding: from 30-50 to 3-5 mm. The smallest pinch (less than 1 mm) affects the grinding.
In the apparatus large, medium and fine crushing are performed, which is referred to as crusher (jaw, conical, etc.).
The choice of milling process and consequently the nature of the crusher depends on the physical properties of the material to be ground and on its size and the size of the shredded product required. For solid and viscous materials, sanding, impact grinding and abrasion are the most reasonable, while fragile materials are recommended by subdivision.
Coarse and medium crushing is mainly done by crushing and splitting, and crushing is done by impact and abrasion.
The diversity of the properties and sizes of the crushed material and the different requirements for the crushed product have led to various types of crushers in which various construction techniques enable the above mentioned crushing processes.
The commutation is used for wide, medium and fine commutation and is carried out between flat, oscillating jaws (horizontal jaw crushers), between eccentrically rounded surfaces (cone crushers) and between rotating rolls (C-roll crushers). ).
 |
| Conveyor are needed to transport materials |
Abrasion, which is always associated with commutation, is performed between rotating grinding wheels, between flat and cylindrical surfaces (tracks g), between curved surfaces of various shapes and used for fine grinding.
A stroke in its pure form is to move the mortar progressively (electronic jolts), turning the rigidly-reinforced fingers (Well Disintegrators) or rotary hammers (3-hammer mills). The shot is used for large, medium and large bruises.
The impact is achieved in combination with abrasion with the help of solids in free fall (and ball and rod mills) and used for fine grinding.
For the crushing of non-ferrous metals, including uranium, the following types of crushers are used: for large scale crushing: jaw crushers and cone crushers; for medium refraction - standard cone crushers and fine crushing - short cone crushers and smooth crusher rolls. All crushers of this type are committed by intermittent ore grinding (jaw crusher) or by continuous pressing (cone crushers, rolls).
Jaw crushers are ground in the space between the movable and fixed jaws of the crusher as the former moves to the second. The material is loaded into the receiving opening of the crusher and drops down to the discharge opening as the size of the pieces decreases.
For cone crushers, in contrast to jaw crushers, crushing occurs continuously between two truncated cones as the moving cone approaches the fixed cone. The frustum-conical crimping section moves along a circle in a solid cone (but does not rotate) and grinds ore pieces by continuous grinding, partly by bending and abrasion.
Roller crushers are used in addition to short cone crushers for fine crushing.
The surface of the rolls can be smooth, grooved and notched. Smooth surface rolls are generally used to grind minerals. The grinding of the material in the smooth surface grinding rolls is produced by crushing the pieces between two rotating rolls.
Roll crushers normally work with dry materials and are a simple, reliable and compact machine that facilitates process control. The use of these crushers is particularly useful when grinding relatively hard and fragile minerals.
Rolling mills have a low productivity and are characterized by a low degree of grinding. Dry grinding produces a lot of dust, which is its disadvantage.
To obtain a material with a particle size of less than 1 mm, fine grinding is used.
The fine grinding according to the following ore processing method and grinding performance can be carried out in the grinding apparatus according to various schemes. For fine grinding in mineral processing, we used grinding machines, webs and backs. In large processing plants, in most cases, fine grinding is carried out in factories.
2. Classification.
The classification is one of the important processes of mineral enrichment, whereby the mixture of mineral grains of different sizes is divided into different contents.
If the classification is done on screens (in the presence or absence of water), this process is referred to as detection and the devices used are detection. If the separation is based on the difference in speed of the grains, which are different in size in water or in the air, the process is referred to as hydraulic or pneumatic classification. The devices used for this purpose are hydraulic classifiers and air separators (tires). ).
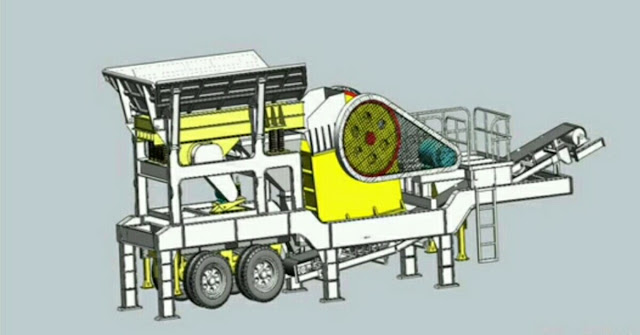 |
| Jaw crusher is one of the machines for processing iron ore |
The purpose of the selection is to obtain a material with certain sizes of pieces or grains; Removal of material whose size is smaller than a certain size; the selection of materials of different types by size for further enrichment, etc. The screening machines used in practice are divided into mobile and stationary screens, with the following four main types of screens: 1) grid, 2) flat vibration, 3) vibration and 4) drum type.
The main part of the sieve work is a sieve or a sieve, with which the material can be divided into two or more classes.
There are three types of screens: parallel grids, perforated or perforated perforated sheets and wire mesh. The materials used are: mild steel, cast iron, stainless steel, bronze, brass, etc.
In practice, the hydraulic classification is performed in a mobile aquatic environment in the form of continuously increasing or horizontal currents and obliquely. Water as a means of transport is used in the classification as a separation, mainly in free fall, and as a means of distribution, mainly in a limited waterfall.
 |
| One of the ore processing factories |
The deposited particles (sands) are removed by means of a transport device, namely reciprocating or spiraling rotations, etc. The undersized material (sands) with closed grinding cycle is returned to the mill for grinding and fine granules in suspension, both the particles and get the water into the plums and then processed. The movement of the transport mechanism causes movement of the pulp and contributes to the classification.
The frame sorter is a narrow and sloped channel which has two side walls and one side and is open at its upper end. One or more rowing sites are placed in the hollow. The frame with crank fits. If you move the comb frame upwards, it is in the lowest position and carries sand. Then he climbs a curve in the highest position and goes down, standing in the sand. Then the curve goes down and the cycle repeats.
The ore classified as pulp is transported to the bottom of the canal. An outflow of particles of the required size is evacuated through the overflow threshold. Sedimented coarse material (sand) is gradually displaced by movements in the channel and discharged through the open upper end.
The spiral classifier according to the working principle is similar to a frame classifier and is a semi-cylindrical channel in which a spiral rotates about the longitudinal axis. The pulp reaches the sedimentation basin and is classified. Fine material in the form of drainage is channeled through the lower end of the sifter channel, while the larger material (sand) settles to the bottom of the channel. collected by a spiral and unloaded at the top of the channel.
Hydro cyclones and centrifuges are used to classify small particles between 5 and 40 micrometers. The classification process in hydro cyclones and centrifuges is greatly accelerated because the centrifugal force, which can exceed gravity by hundreds and thousands, is used to precipitate mineral particles in a liquid medium.
A hydro cyclone consists of a reverse metal cone with a flat cover and a central outlet for drainage.
The food in the form of pulp is fed through a centrifugal sand pump located in the cylindrical part of the apparatus through a pipe whose cross-section decreases as it enters the cyclone. Large particles are collected in the top of the cone and discharged through the outlet of the nozzle, while the finer ones emerge through the drain hole.
The pulp entering a hydro cyclone tangent to the inner surface of the cone forms a helical stream which contracts downwards and divides at a point on the cone. High in the main stream exits the upper drainage hole. In the middle of the cyclone, a cylindrical column of air forms along its vertical axis.






No comments:
Post a Comment